De-dollarization efforts are accelerating right now as Algeria officially joins the BRICS New Development Bank, and this marks a significant shift away from US dollar dominance. This BRICS expansion strengthens local currency initiatives and also drives currency substitution trends, challenging traditional Western financial systems through the growing influence of the BRICS bank.
Also Read: De-Dollarization: 9 Countries Ditch the US Dollar
How BRICS Expansion And Local Currency Use Drive Currency Substitution Trends

With Algeria now part of the New Development Bank, the move away from the dollar is gathering strength and BRICS expansion stands for not only expanding the bank but also encouraging trading with local currencies and other bypass methods.
NDB President Dilma Rousseff had this to say:
“boost the bank’s global influence and strengthen its mission to support sustainable development without reliance on traditional Western financial structures”
Algeria Strengthens BRICS Bank Alternative System

Algeria’s membership in the BRICS bank comes as emerging economies are intensifying their de-dollarization strategies right now. The North African nation’s decision demonstrates how currency substitution efforts are spreading beyond the original BRICS members, with more countries seeking local currency alternatives and also trying to reduce dependence on the united states dollar.
At this time, the BRICS is growing wider even as there are many criticisms of the IMF and World Bank for their Western-led policies. At the time of writing, many oil- and resource-rich countries, including Algeria, are increasingly aligning with the NDB as a result of boosted efforts to weaken the US dollar.
Also Read: De-Dollarization: 5 Oil Giants Now Settling in Yuan, Not USD
Currency Substitution Accelerates Through BRICS Currency Initiatives
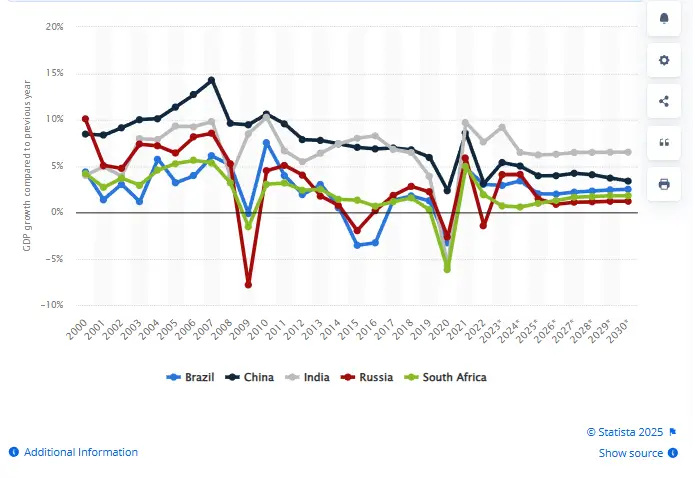
The de-dollarization push through BRICS bank expansion creates viable pathways for local currency trading, and countries like russia and also china lead these currency substitution efforts. They are establishing alternative payment systems that support the broader BRICS currency vision for multipolar finance right now.

Through the participation of Algeria in BRICS, the ASF can now safely finance key infrastructure projects in the Global South, leaving aside customary American dollar-based methods.
Also Read: De-Dollarization: 7 Global Deals That Shut Out the Dollar
More countries choosing to join the NDB suggests currency substitution will increase and efforts to replace the dollar will gain speed. This is potentially going to shift the focus of global finance from a Western approach to locally used currencies and involvement from several leading countries, as at this time.