Leading economic groups now challenge US dollar dominance by creating their payment networks. De-dollarization is being led by BRICS, ASEAN, the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) as they build comprehensive new systems for trading in local currencies.
These groups work to reshape the global financial system through coordinated efforts and innovative payment solutions.
Also Read: Meta (META) Q3 Earnings: Record Highs & Heavy Spending – What’s Next?
Global Finance Shifts: Countries Embracing De-Dollarization
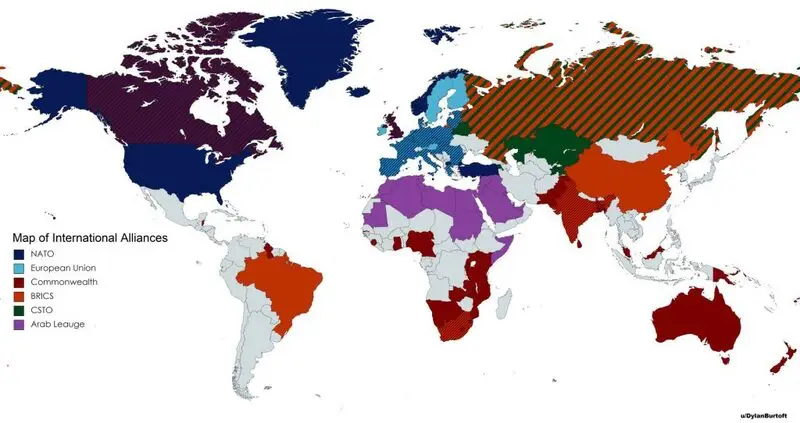
BRICS Nations
China
China‘s payment system, CIPS, now connects over 1,300 banks worldwide. Daily transactions grew 50% in 2022 after Russia entered Ukraine, then rose another 25% in early 2023. This was an important de-dollarization step.
UnionPay cards now work in 180 countries, with 7.5 billion cards in use—more than Visa and Mastercard combined. Yuan payments now make up 47% of China’s international trades, showing significant progress in reducing dollar dependency across Asian markets.
Russia
Russia cut its US dollar holdings by $101 billion and built SPFS to replace SWIFT. By May 2023, thirty Russian banks had joined CIPS, and 70% of trade with China had used yuan.
Russia’s MIR payment system serves 10% of Russians through 13.9 million cards. Between 2022 and mid-2023, payments in rubles jumped from 10% to 40%, marking a substantial shift in Russian trade practices and financial independence.
Also Read: Can Ethereum Hit $3,000 in November 2024?
India
By August 2023, banks from twenty countries opened special rupee accounts in India, initiating the official de-dollarization process. This includes thirty-four Russian banks working with fourteen Indian financial institutions.
India has signed comprehensive agreements with the UAE and Saudi Arabia to use rupees and dirhams for trade. Due to rupee price changes, oil buyers prefer dirhams, leading to significant shifts in energy trade payments.
Brazil
Brazil opened its first yuan clearing bank in 2023 and joined CIPS through a strategic partnership. At 5.37%, the yuan now makes up more of Brazil’s reserves than euros, demonstrating the country’s commitment to currency diversification and thus contributing to de-dollarization.
The government recently completed its first direct trade using yuan and reals, establishing new pathways for South American commerce.
ASEAN Integration
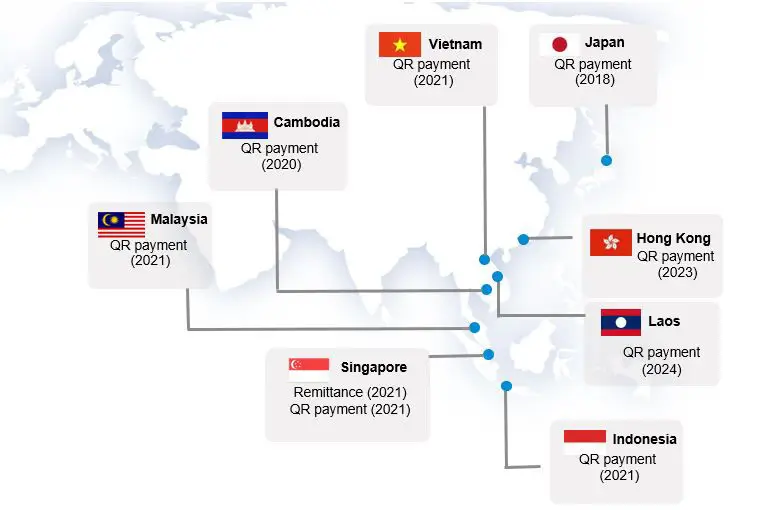
ASEAN’s QR code system launched in September 2023 cuts payment costs by 30% across member states. The 42nd ASEAN Summit approved this system, extensive plans for electric vehicles, and enhanced security measures. These changes help protect against financial vulnerabilities and potential sanctions like those affecting Russian assets.
Cambodia
Cambodia grows through electronics manufacturing exports and strategic economic development. Its central bank requires increased foreign currency reserves while implementing new financial policies. Growing tourism helps strengthen the local currency through sustained economic activity.
Indonesia
Through bilateral agreements, Indonesia trades in local money with China, Malaysia, Thailand, Japan, and South Korea. Its QRIS system helps 3.6 million small businesses use local currency for payments, promoting financial inclusion and regional integration.
Thailand
Through groundbreaking agreements, Thailand started trading in local currencies with Indonesia and Malaysia in 2016. Tourism and foreign investment still need dollars, but the central bank works actively on regional payment connections and financial infrastructure development.
Also Read: Pundit Predicts 3 Altcoins to Outperform XRP and Cardano
Economic Pressures
When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, developing countries face mounting challenges. Money leaves these countries, and debts cost more to repay, creating significant economic strain. This increasing pressure pushes countries to find alternatives to the dollar system and develop independent financial mechanisms.
CIS Integration
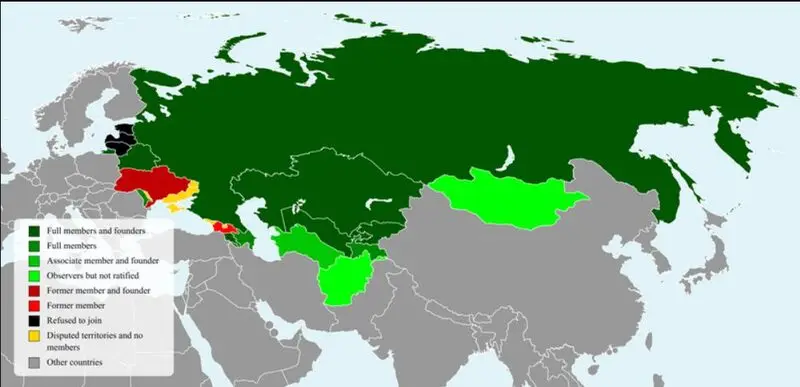
Belarus now fully uses Russia’s SPFS system for regional transactions. Armenia increased local currency trading through CIS banks and financial networks.
Both countries rely less on Western financial systems and strengthen regional banking connections through innovative payment solutions and integrated messaging systems.
As you can see, the de-dollarization process is ongoing. We’re curious to see how this situation will evolve.






